Unmasking Imposter Scams: A Dive into Social Engineering and Spoofing Tactics
Imposter scams have emerged as a dominant force in cyber-enabled fraud, eclipsing traditional phishing in terms of scale and impact. By leveraging social engineering tactics, spoofing technologies, and psychological manipulation, attackers deceive victims into divulging sensitive information or transferring funds.
Social Engineering Techniques:
- Exploiting human psychology: manipulating trust, fear, urgency, or perceived authority
- Caller ID spoofing: using VoIP tools to mimic legitimate numbers
- Phishing pages: cloning official sites using tools like HTTrack or Evilginx
- Email spoofing: exploiting SMTP vulnerabilities or using tools like SendEmail and SET Toolkit
- SMS spoofing: abusing compromised or unauthorized SMS gateways
- Impersonation on messaging platforms: replicating profile pictures and usernames on platforms like WhatsApp
- Deepfake voice and video: using advanced tools like ElevenLabs or Descript to mimic real individuals
Malware and Phishing Attacks
- Malware delivery: delivering spyware or remote access trojans (RATs) like njRAT or Quasar via malicious links
- Vishing (voice phishing): live callers deceiving victims into disclosing sensitive data like OTPs and PINs
Technical Aspects of an Imposter Scam
| Aspect | Details |
| Social Engineering | Core technique used—fraudster exploits trust, fear, urgency, or authority |
| Caller ID Spoofing | Fraudster uses VoIP tools (e.g., Asterisk, FreePBX, SpoofCard) to fake legitimate phone numbers |
| Phishing Pages | Clone sites (banks, tax dept) built using tools like HTTrack, Evilginx, or custom HTML+PHP |
| Email Spoofing | Uses SMTP vulnerabilities, tools like SendEmail, SET Toolkit, or fake headers to forge senders |
| SMS Spoofing | Uses SMS gateways or APIs (unauthorized or compromised) to send messages from fake sender IDs |
| WhatsApp Impersonation | Cloning profile pic, name, and sending messages from similar numbers |
| Deepfake Voice/Video | Rare, but growing—voice cloning tools (e.g., Respeecher, Descript, ElevenLabs) used in scams |
| Malware | Embedded links install spyware, remote access trojans (RATs) like njRAT, Quasar, DarkComet |
| Vishing | Voice phishing—live calls tricking victim into revealing OTPs, PINs, etc. |
| Fake Apps | Fraud apps with UI mimicking real ones; often built using Android Studio or MIT App Inventor |
| Remote Access | Scammer may ask to install apps like AnyDesk, TeamViewer, or QuickSupport for full phone control |
| Fake Payment Proofs | Use photo editing tools like Photoshop or fake payment generator apps to show “proof” |
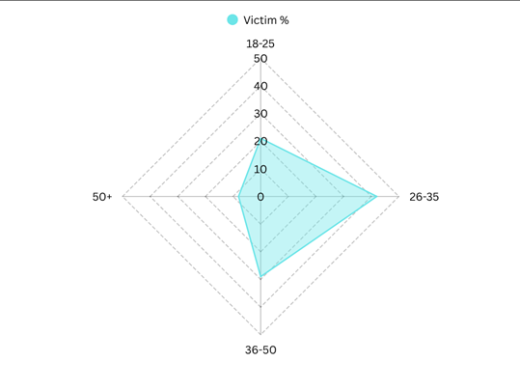
Age group Distribution :
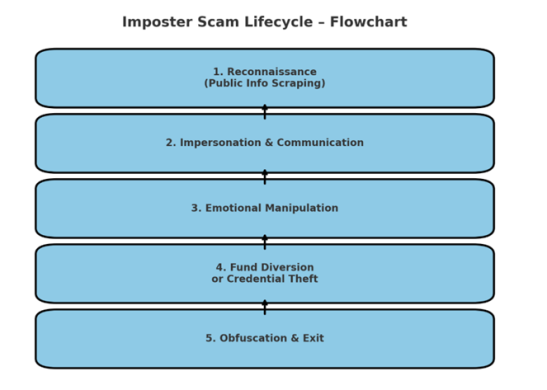
Classification of Imposter Scams :
| Type | Description |
| Tech Support Fraud | Fake security alerts with remote access malware (AnyDesk, TeamViewer) |
| Bank Imposter Scams | OTP or PIN harvesting under pretense of “fraud alert” or “KYC update” |
| Romance Scams | Emotional bonding followed by financial requests |
| BEC (Business Email Compromise) | Fake invoices or vendor payment instructions with real-looking domains |
Technical Attack Vectors
- Caller ID Spoofing: Faking phone number metadata to appear legitimate.
- Email Spoofing / Typo squatting: Creating fake email addresses with slight variations.
- Link Obfuscation: Hiding malicious URLs behind shortened or encoded links.
- Remote Control Tools: Tricking victims into installing screen-sharing tools.
- Voice AI Deepfakes: Using cloned voices to impersonate real individuals.
Statistical Overview :
| Region | Losses (2024) | Median Loss | Growth YoY | Source |
| USA | $2.6 Billion | $1,000 | ↑ 18% | FTC Consumer Sentinel |
| India | ₹950 Crores | ₹28,000 | ↑ 32% | CERT-IN/NCRB |
| UK | £580 Million | £2,000 | ↑ 15% | Action Fraud UK |
Popular Communication Channels:
| Channel | Usage (%) |
| Phone Call | 43% |
| 25% | |
| SMS/ WhatsApp | 22% |
| Social Media | 10% |
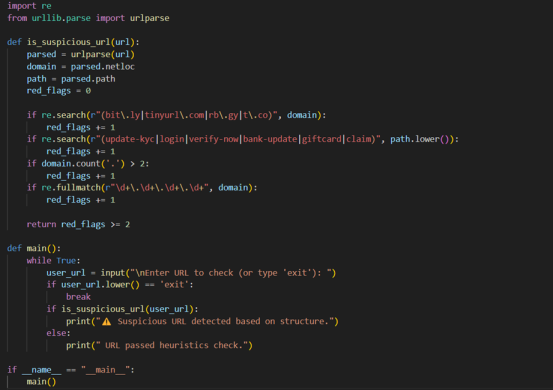
A Basic Heuristic-Based Real-Time URL Scam Detection mechanism :
Real Life Incidents of Imposter Scams :
Note : The incidents were sourced from credible news platforms including India Today, Times of India, and The Hindu, covering verified cybercrime reports from 2025.
- AI Deepfake IPS Officer Scam — ₹78.6 Lakh
- Fraud Period: July 2–7, 2025, during which transfers occurred.
- Case Reported: July 8, 2025 at Kranti Chowk Police Station in Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar.
- Location: Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar (Aurangabad), Maharashtra
- Modus Operandi:
- Victims (elderly couple) received a video call with an AI-generated deepfake of IPS officer Vishwas Nangare Patil. They were told they were involved in terrorism-related money laundering.
- Technology Used: Deepfake AI, WhatsApp VoIP, Caller ID spoofing.
- Impact: ₹78.6 lakh lost.

2. ₹3.18 Lakh Crore Digital Investment Scam (Maharashtra)
Revelation Date: July 4, 2025, during a Maharashtra Legislative Council session by Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis, disclosing overall estimated losses and investor figures.
- Modus Operandi:
- Investors were lured into fake crypto, forex, and stock platforms with huge ROI promises.
- Money funneled through shell companies, mule accounts, and foreign crypto exchanges.
- Hundreds of accounts frozen, but majority of the money untraceable.
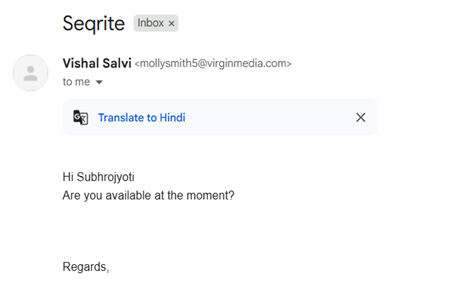
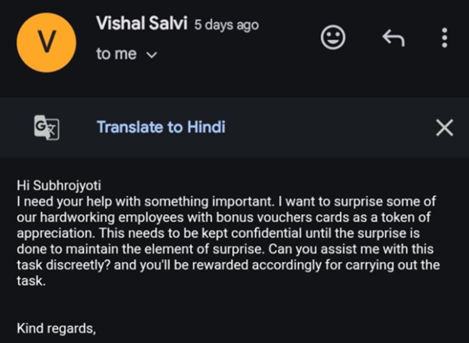
3. CEO WhatsApp Scam — ₹7 Crore Lost by Delhi Companies
- Reported Victim Transfer: January 7, 2025 (funds transferred believing fake WhatsApp CEO message).
- FIR Filed: February 4, 2025, at South Region Cyber Crime Police Station in Mumbai.
- Location: Delhi, NCR
- Modus Operandi:
- Finance officers received WhatsApp messages from a fake CEO profile with company logo and profile photo.
- Urgent requests for vendor payments made to mule accounts.
- Companies transferred large amounts without voice verification.
- Tech Used: WhatsApp Business cloning, logo forging, social engineering.
4. Sambalpur Family Investment Scam — ₹88 Lakh
Police Action / Arrests: August 5, 2025, four suspects arrested in Sambalpur following the fraud against Ramesh Chandra Biswal’s family.
- Location: Sambalpur, Odisha
- Modus Operandi:
- Victim family lured via Telegram group run by fraudsters posing as SEBI-registered stock experts.
- They deposited money gradually through UPI, crypto wallets, and online trading apps.
- Access to “profit dashboard” given, but withdrawals were blocked.
- ₹70 lakh traced across 13 mule bank accounts.
- Tools Used: Telegram bots, fake trading platforms, WhatsApp spoofing.
Detection Mechanism :
- High-pressure tactics: Scammers create a sense of urgency or threat to rush you into action.
- Secrecy requests: Imposters ask you to keep the conversation secret.
- Spoofed caller ID or email: Scammers manipulate caller ID or email to appear legitimate.
- Inconsistent tone or language: Poor grammar, generic greetings, or overuse of official-sounding words.
- Unverified requests for sensitive info: Scammers ask for OTP, bank PIN, Aadhar, PAN, or payment via gift cards, cryptocurrency, or UPI.
- Fake websites or phishing pages: Scammers create similar-looking URLs to government or bank portals.
- AI-cloned voice or speech synthesis: Scammers use AI to mimic known individuals or create fake audio/video messages.
- Digital footprint analysis: Monitoring repeated complaints, domain/IP logs, or VoIP activity can help detect scams.
- Unusual account activity: Login attempts from new locations/devices or sudden changes in communication patterns.
- Spoofed messages: Fake messages from “official” handles without verified checkmarks or shortened URLs.
Technical Detection Methods:
| Technique | Description | Tools/Methods |
| NLP Classifiers | Identify scam-like phrases using text classification | TF-IDF + Logistic Regression, BERT |
| Regex Filters | Match patterns in URLs or emails to detect scams | Python re, domain blacklists |
| Link Risk Scoring | Assess domain credibility via age, WHOIS, and SSL checks | VirusTotal API, Scamalytics, urlscan |
| Anomaly Detection | Flag unusual transaction patterns using machine learning | Isolation Forest, k-Means, XGBoost |
| Voice Fingerprinting | Detect AI-generated robocalls using audio analysis | OpenL3, Google VocoNet |
QUICK HEAL ANTIFRAUD.AI DETECTION
| Use Case | How AntiFraud.AI Helps |
| Voice Scam Detection | Analyzes call metadata and speech patterns |
| SMS/Phishing Link Detection | Flags malicious URLs or keywords in SMS/WhatsApp |
| QR Phishing | Identifies suspicious QR codes and decoding redirection URLs |
| Behavioral Anomaly Detection | Detects sudden fund transfers or out-of-pattern user actions |
| KYC/BFSI Fraud | Validates links, caller numbers, or requests pretending to be banks |
Conclusion : Imposter scams are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging technology and psychological manipulation to target people of all ages and backgrounds. These scams can cause devastating financial losses and emotional distress. To protect yourself, it’s crucial to be aware of the tactics scammers use, detect warning signs, and exercise caution in your digital interactions. Staying informed and vigilant is key to safeguarding personal and organizational security in today’s evolving cyber threat landscape.








