
Nov

Pig Butchering Scams: Inside a Rapidly Growing Global Fraud Operation
-
Pravesh Shinde / 3 months
- November 27, 2025
- 0
Pig Butchering scams have emerged as one of the most damaging forms of modern online fraud, blending long-term social engineering, emotional manipulation and sophisticated fake investment infrastructure. Named after the strategy of “fattening the pig before slaughter,” these scams rely on building strong trust with victims before pushing them into high-value financial traps. Over the past year, Seqrite Labs has tracked a sharp rise in such campaigns targeting Indian users through WhatsApp, Instagram, Telegram and dating platforms.
Pig Butchering Scam also known as a “Sha zhu pan” scam, is a type of online investment fraud that involves scammers creating fake online personas to lure victims into fraudulent investment schemes.
How the Scam Begins
Attackers start by identifying targets from leaked databases, scraped social media profiles or random messaging campaigns. Initial contact usually appears harmless: a casual greeting, a friendly introduction or a “wrong number” message. These approaches are carefully designed to avoid suspicion and create opportunities for prolonged conversation.
Relationship Building & Emotional Grooming
Once the victim responds, scammers invest significant time in developing rapport. They often present polished personas supported with stolen or AI-enerated photos, curated lifestyle stories and scripted conversations. Their communication is consistent and empathetic, making the victim feel valued and emotionally comfortable. This grooming stage can last weeks, ultimately lowering the victim’s skepticism and enabling deeper manipulation.
Introducing the Investment Hook
When trust is well-established, scammers slowly introduce the idea of investing. They often claim to have expertise in cryptocurrency trading or access to exclusive financial
opportunities. Victims are shown screenshots of impressive but fabricated returns and may be encouraged by fake stories of personal success. This shift is subtle at first but becomes increasingly assertive as the scammer senses vulnerability.
Fraudulent Trading Platforms
Victims are guided to fake trading apps or websites that closely resemble legitimate exchanges. These platforms often include:
· Real time charts pulled from public APIs
· Attractive dashboards showing growing balances
· Customer support operated by the scammer group
· Multiple investment tiers such as “VIP”, “Silver”, or “Family Plan”
All data displayed is entirely fabricated. Profits, balances and transaction confirmations are generated server side to create a false sense of legitimacy.
Escalation & Financial Extraction
Victims initially invest small amounts and often see quick, seemingly real returns. Some platforms even allow small withdrawals to build trust. Once the victim becomes confident, scammers push for larger deposits through limited time offers, “market alerts” or the promise of higher yield opportunities. This escalation continues until the victim either reaches their financial limit or becomes suspicious.
Withdrawal Blocking
When victims attempt to withdraw significant amounts, the platform starts displaying errors:
· “KYC verification pending”
· “Tax payment required”
· “Account under review”
Support becomes unresponsive, and the scammer disappears from all communication channels. At this point, all invested money is effectively lost.
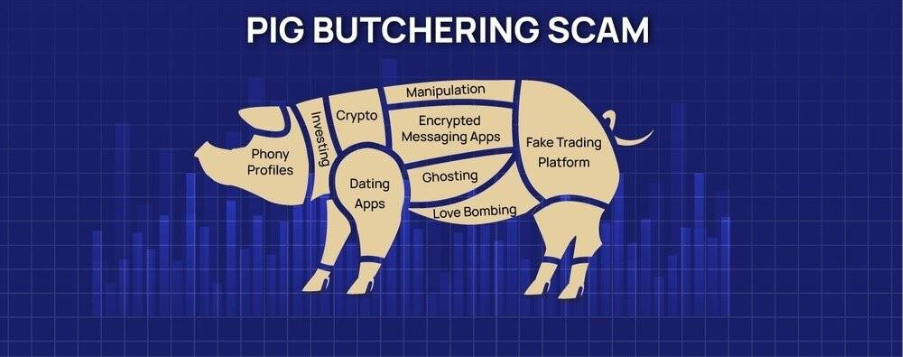
Pig Butchering scams follow a carefully orchestrated sequence designed to manipulate victims over time. The process typically begins with the “host” reaching out through social media, dating platforms, or cleverly crafted unsolicited messages. Once a potential target referred to as the “pig” responds, the scammer gradually builds a false sense of trust, often posing as a friend, mentor, or romantic interest.
After establishing rapport, the scammer introduces the idea of cryptocurrency trading, claiming to have exclusive knowledge or access to high return opportunities. Victims are then directed to use fraudulent trading websites or apps that display fabricated profits and manipulated market data, creating the illusion of legitimate success.
As the victim becomes more confident, the scammer slowly encourages larger investments, a method commonly described as “fattening the pig.” This continues until the victim has deposited a substantial amount of money.
The scam is exposed only when the victim attempts to withdraw their funds. At this stage, the fake platform either blocks withdrawals, demands excessive “taxes” or “fees,” or abruptly shuts down. Due to the irreversible nature of blockchain transactions and the anonymity exploited by scammers, recovering lost funds becomes extremely challenging.
Key Signs You’re Dealing With a Pig Butchering Scam
1. “Wrong Number” Texts That Randomly Turn Social Media
· Scammers often begin with a casual “Hi, is this Riya?” or “Didn’t we meet at the café?” message.
If you reply, they smoothly shift into conversation and try to build familiarity.
2. Extremely Fast Emotional Bonding
· Within days they act overly friendly, caring, or flirty.
· They reply instantly, share attractive photos, and over invest in the friendship, basically love bombing with a strategy.
3. Too Much Personal Interest in Your Finances
They subtly ask:
· “Do you save or invest?”
· “Are you into crypto?”
· “Do you want to grow your money faster?”
Secondary Scams
Many victims are later contacted by fake investigators, law enforcement impersonators or recovery agents claiming they can retrieve the lost money. These “recovery scams” demand an upfront fee or identity documents, exploiting the victim a second time.
Technical Infrastructure Observed(the layout followed by scammers)
Seqrite Labs analysis shows that most Pig Butchering platforms rely on:
· Short-lived domains with privacy enabled WHOIS
· Offshore VPS hosting
· SSL certificates from free providers
· API endpoints serving static or pre-scripted financial data
· APKs distributed outside official app stores
Communication typically occurs over WhatsApp, Telegram or Instagram, using disposable VoIP numbers and Ai enhanced profile photos.
Real life stories
Pig Butchering scams continue to devastate victims across the world, cutting across age, profession, and education level. These cases highlight how even smart, financially aware individuals can be manipulated when scammers strike during vulnerable moments.
In one case, an Indian IT professional working in Philadelphia was targeted on a dating app by a scammer using deepfake videos and scripted emotional manipulation. Posing as a French wine trader, he built an intense romantic connection and gradually persuaded her to invest in fake crypto platforms. She ultimately lost more than $450,000, leaving her in crushing debt.
Another victim a Malaysian nurse working in Singapore fell for a scammer who exploited her loneliness during pandemic restrictions. Believing she was investing for a shared future, she
funneled money into a fraudulent platform using loans, personal savings, and even a mortgage. The scam drained her financially, forcing her into bankruptcy.
A third case involved a family man from Denver who believed he had earned millions through a trading app promoted by a woman he met online. When he tried to withdraw his supposed profits, the platform locked him out and demanded additional payments. He lost $1.6 million his entire retirement savings.
These stories underscore the emotional precision and financial devastation behind Pig Butchering scams.
Preventive Measures
For individuals:
Avoid engaging with unsolicited messages, especially those that begin with “wrong number” introductions or friendly small talk. These seemingly harmless texts are often the entry point for social engineering attempts, where scammers slowly build trust before introducing fraudulent investment opportunities. Ignoring or blocking unknown contacts is one of the easiest ways to cut off the scam before it starts.
Do not trust financial advice from online acquaintances or people who claim to have insider knowledge on crypto, trading, or high return schemes. Scammers deliberately present themselves as successful investors or mentors, but their real goal is to nudge you into platforms they control.
Always verify any trading or investment platform directly through official regulatory authorities such as SEBI or other financial regulators. Legitimate platforms are licensed, transparent, and publicly searchable. Fake platforms often mimic real exchanges but lack proper registration or compliance.
Finally, avoid installing sideloaded or non-store investment apps, even if someone insists that they offer “better returns” or “exclusive access.” Apps outside trusted stores are not vetted for security and can easily display fake profits, steal credentials, or lock your funds. Sticking to verified sources and official app stores is essential to staying safe from Pig Butchering style scams.
For organizations:
Organizations can significantly reduce the impact of Pig Butchering scams and other financial frauds by strengthening user awareness and security hygiene. Conducting regular cybersecurity awareness sessions is essential, as it helps employees recognize social
engineering techniques, fraudulent investment approaches, and red flags associated with unsolicited financial communication. Well informed users act as the first line of defence.
In parallel, security teams should continuously monitor for scam domains, fake trading websites, and malicious APK distribution channels. Threat actors frequently rely on typo squatted domains and off store apps to lure victims, making proactive monitoring critical for early detection and blocking.
Implementing robust endpoint protection is another key layer. Modern security solutions can automatically block access to fraudulent websites, detect malicious payloads in unauthorized APKs, and prevent users from interacting with untrusted financial platforms. This minimizes the risk of accidental exposure or compromise.
Finally, organizations should encourage timely reporting of suspicious financial outreach. Whether it’s an unusual text, an unexpected investment offer, or a request to install a third party trading app, quick reporting allows security teams to investigate and respond before the threat escalates. Together, these measures create a strong defence posture against evolving digital fraud schemes.
Conclusion
Pig Butchering scams combine advanced psychological manipulation with technical sophistication, making them one of the most dangerous fraud models today. With India witnessing increasing incidents, awareness and proactive cyber hygiene are crucial. Seqrite Labs continues to monitor these campaigns and provide actionable intelligence to help users and organizations stay protected.
In the world of Pig Butchering scams, the biggest takeaway is simple: trust shouldn’t be outsourced to strangers on the internet especially when money’s involved. If someone you barely know tries to mix emotions and investments, that’s your cue to step back, breathe, and verify. Real opportunities don’t come with pressure, secrecy, or “too good to be true” returns.
Your guard is your greatest firewall. Stay alert, question everything, and remember if a stranger is overly interested in your feelings and your finances, they’re not building a bond, they’re building a trap.
References ·
- https://vajiramandravi.com/current-affairs/pig-butchering-scam/ ·
- https://www.investopedia.com/pig-butchering-scams-8605501
- www.equentis.com
Contributors:
· Deepak Patil
· Krishna Arun Iyer
· Rahul Kumar Mishra






